BUILD YOUR OWN MODULAR
Back to main to BYOM pageDETAILED MIXER ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
This page is dedicated to detailed photographic step-by-step instructions for the assembly of the mixer module in the BYOM kit. It is not necessary to follow the order of these steps, but I recommend doing it if you are just starting out as I attempt to do it in the easiest order. Take your time, a small mistake can sometimes cause hours of debugging! If it is not working, take a break and then come back and check again.
BILL OF MATERIALS
Here are the bill of materials for this module, they should be obtained from the main bill of materials that is printed in the book and on the root page of BYOM website. It is better to use the tick box sheet provided in the book whilst going along, but it is provided here as extra reference. Essentially the reference’s refer to the printed component locations on the board. The book contains images and descriptions of each component so use that if you are not familiar to what part the value is referring to.
| Reference | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|
| C1, C2 | 100nF 5mm Ceramic | 1 |
| R10 | 1KΩ 1/4W resistor | 2 |
| R1,R2,R3,R4,R5,R6,R7,R8,R9 | 100kΩ 1/4W resistor | 9 |
| D1, D2 | 1N5817 DO-41 diode | 2 |
| U1 | TL074 IC | 1 |
| U1 Socket | DIP 14 Socket | 1 |
| J5 | IDC socket 10 pin | 1 |
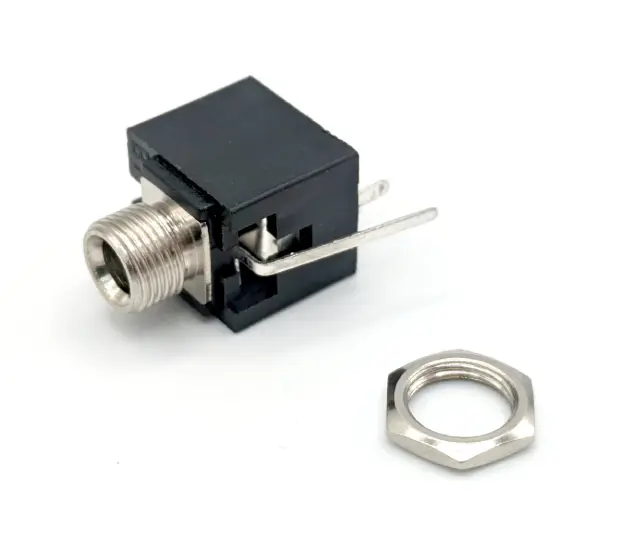
| J1, J2, J3, J4 | Thonkiconn PJ398SM | 4 |
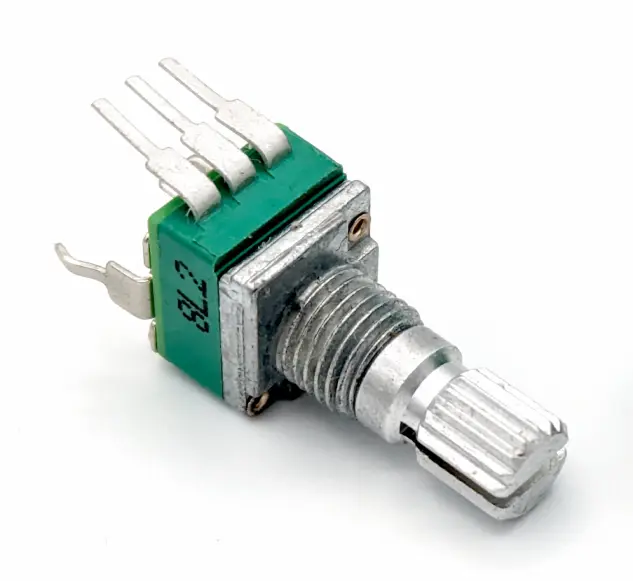
| RV1, RV2, RV3 | B100KΩ 9mm Vertical Potentiometer | 3 |
ASSEMBLY
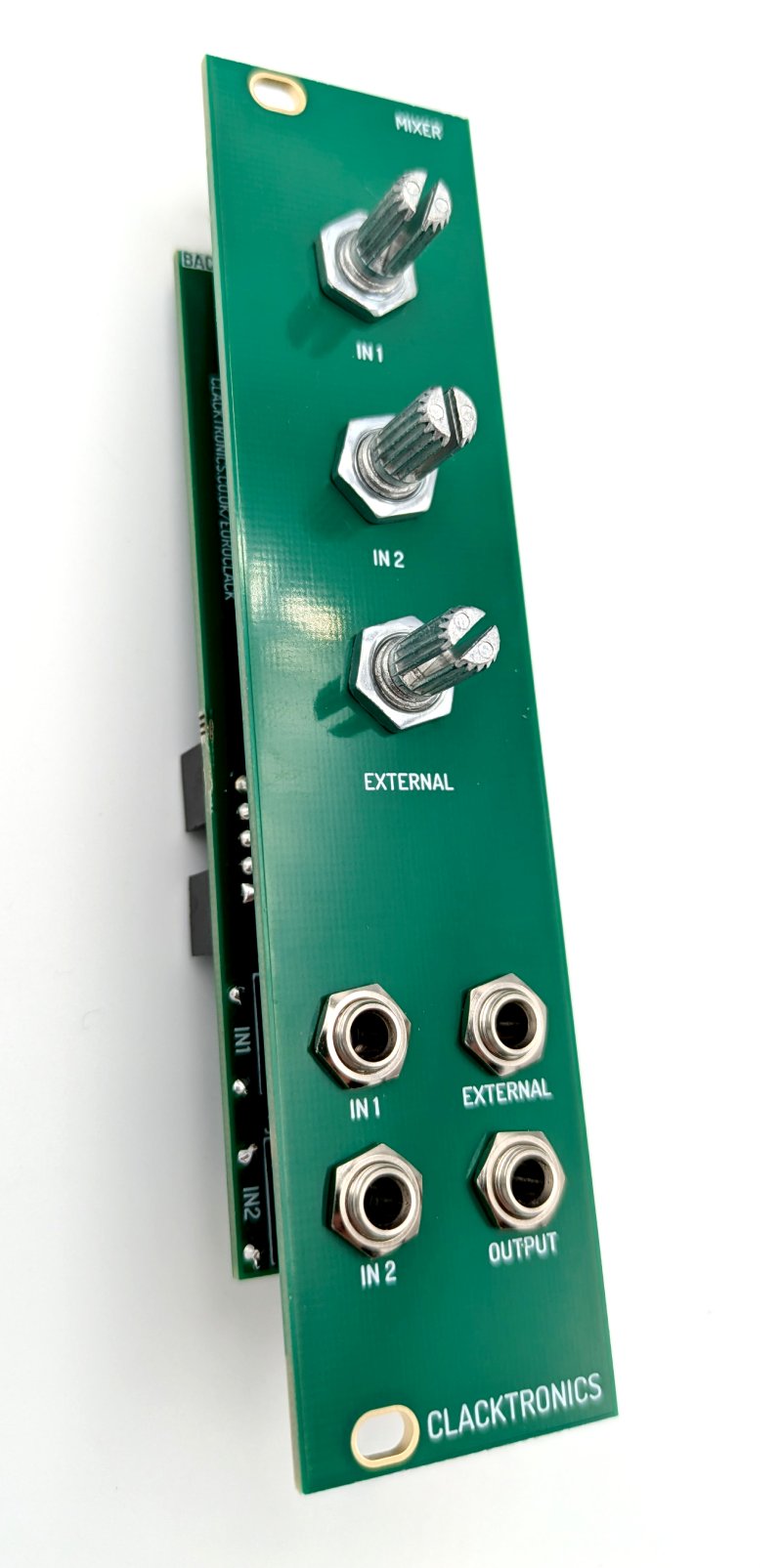
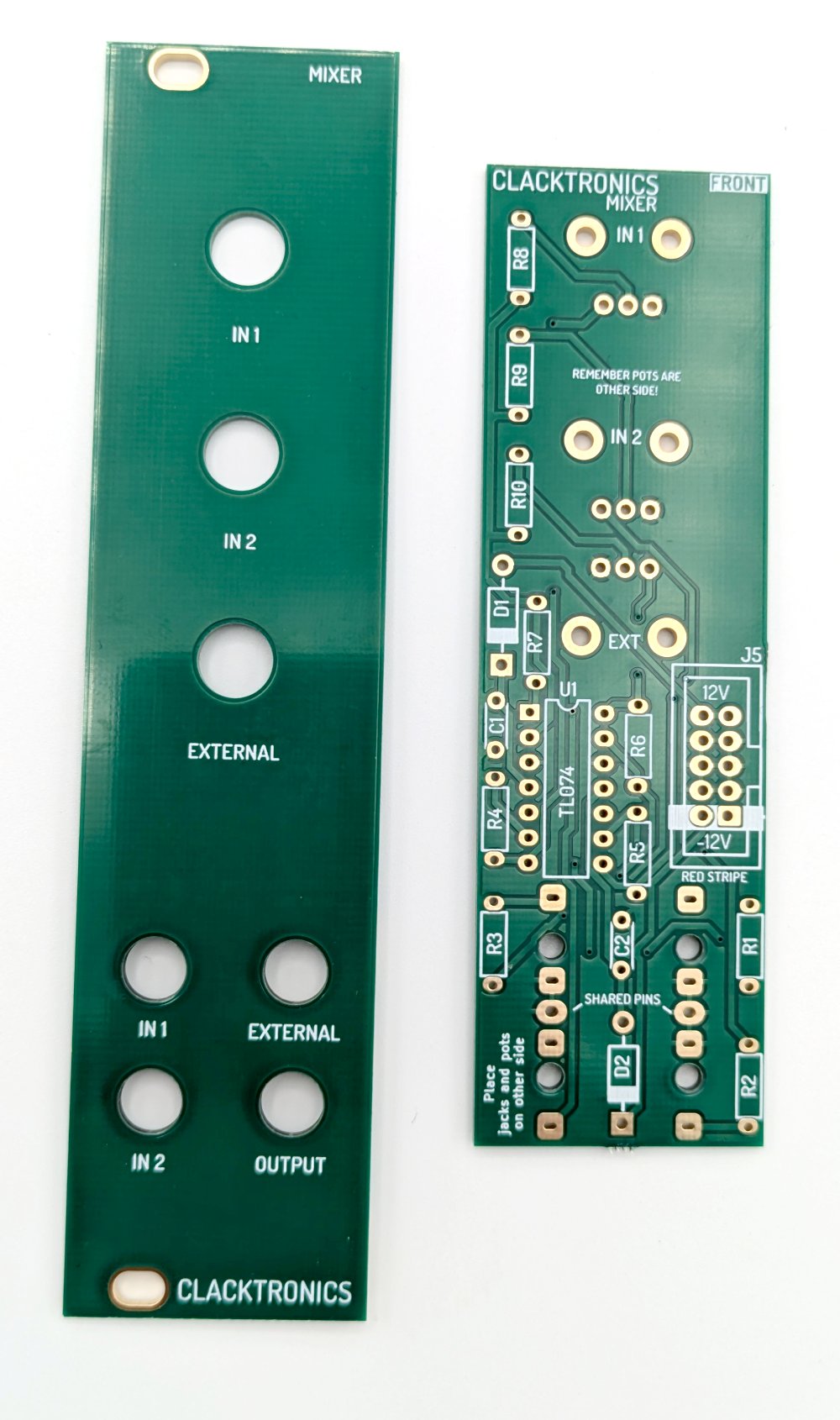
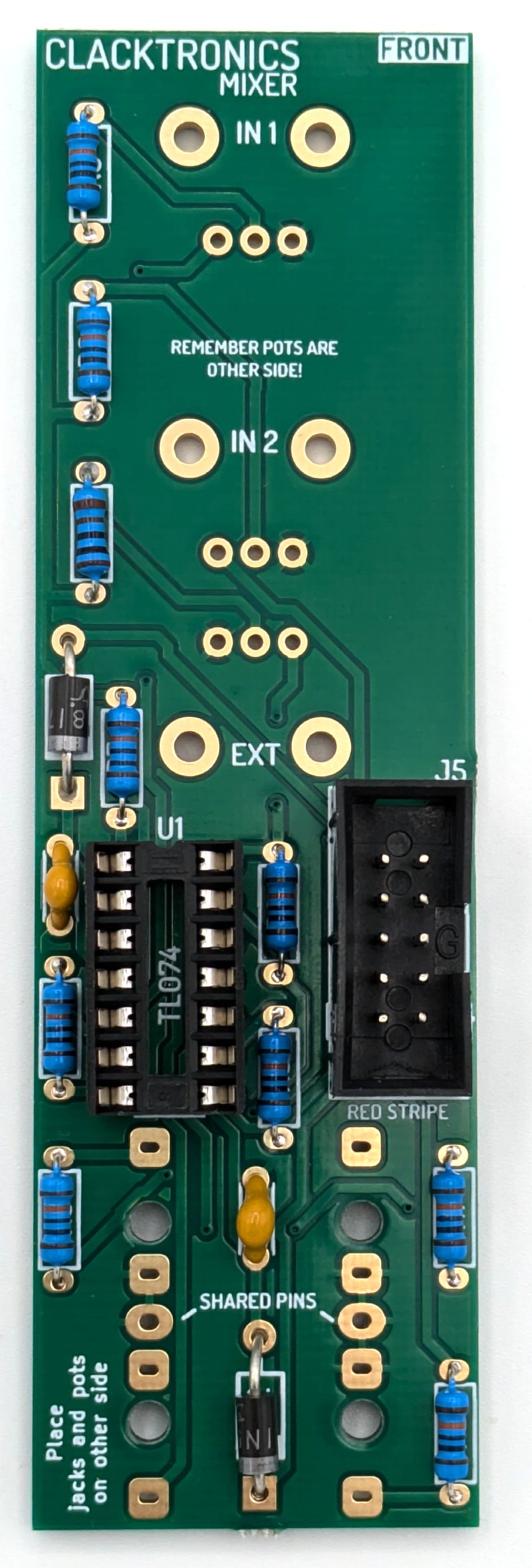
You must start with the two mixer PCBs, the front panel and the main PCB as pictured.
STEP 1 : RESISTORS
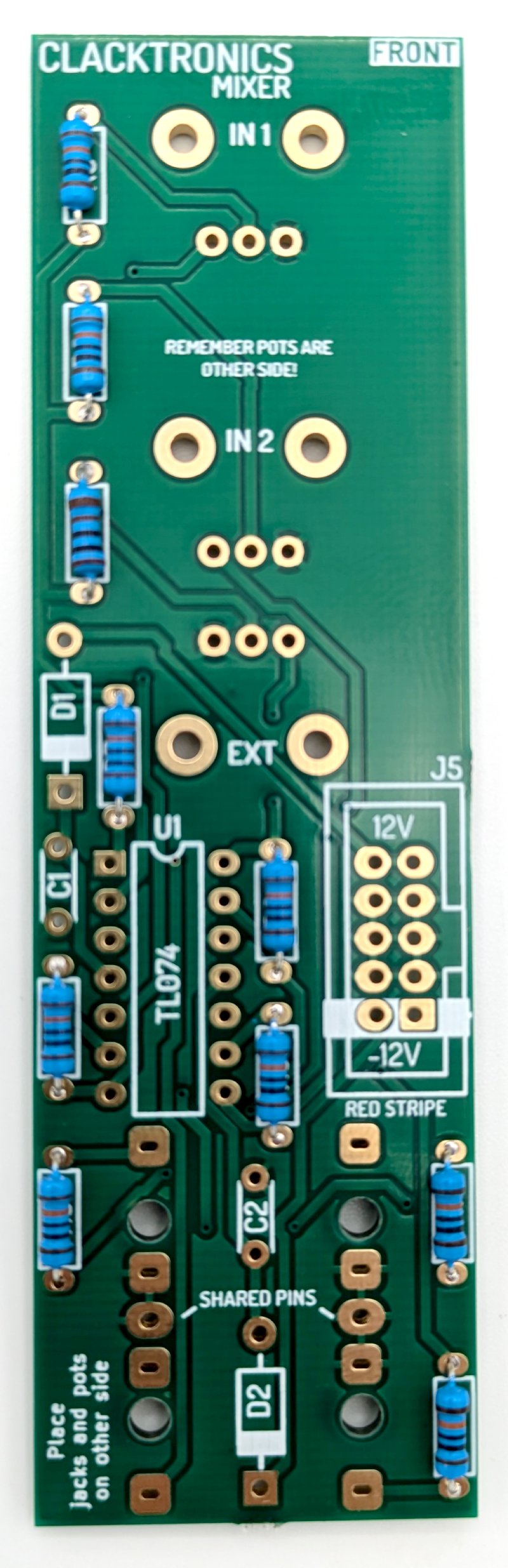
Install the resistors first, as these components can be in some awkward places after connectors have gone on. Make sure you are installing on the "FRONT" mark side of the board. Bend the leads of the resistors as tight as you can up to 90 degrees as they will only just fit in, this was to save space on the board. This board is quite simple there are 10 resistors and 9 of them are 100kΩ and the other is 1kΩ.


Above are the two values needed, use the BOM within the book and tick off the resistors as you go along. Note the way the resistors look can vary quite a lot. There is no orientation to the resistors, they can go either way around, be sure to be installing them on the "FRONT" side of the panel.
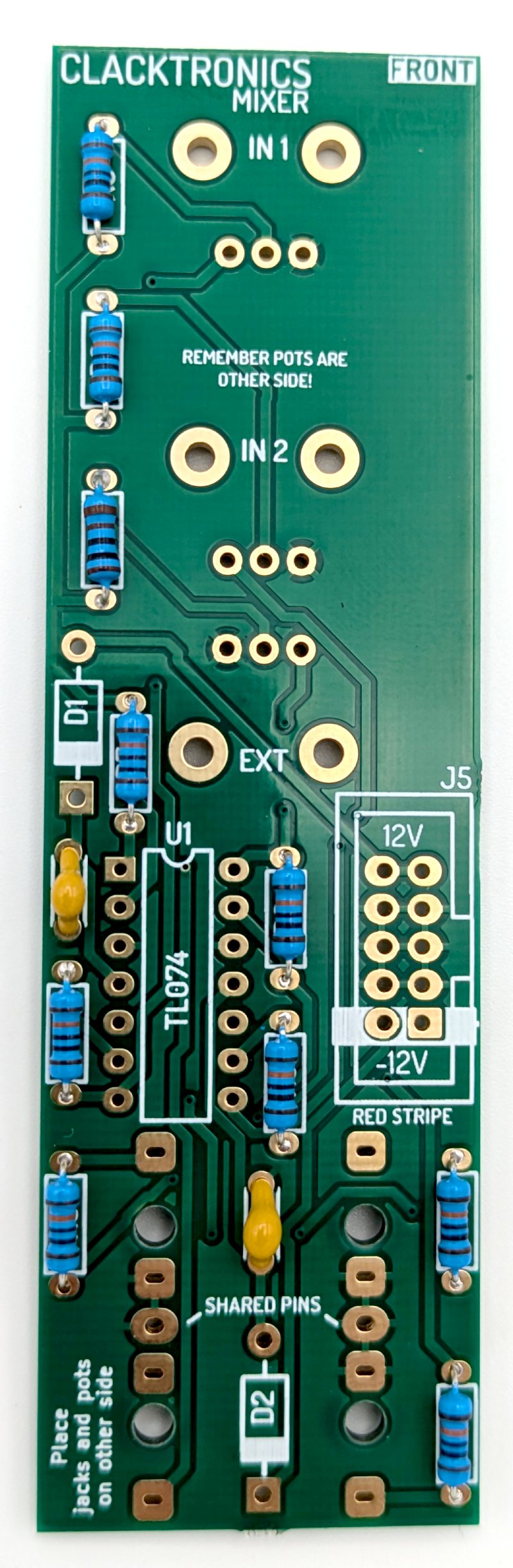
STEP 2 : CAPACITORS
These are multilayer caramic capacitors (MLCC), there is only one value of 100nF in the mixer. They are simply here to provide some decoupling. Again there is no orientation to these two pin parts, put them in either way around, I like to try and keep their value visible from the side so face them outwards. They should be marked with 104 which means 10 x 4 pico farads, equals 100000pF aka 100nF. Your capacitor may be marked different, sometimes you get 0.1 marking which is the same value in microfarads instead.

Note your capacitor may be a different colour, or marking than this capacitor as there is variation between different manufacturers. If you ordered them yourself, check the manufacturers datasheet.
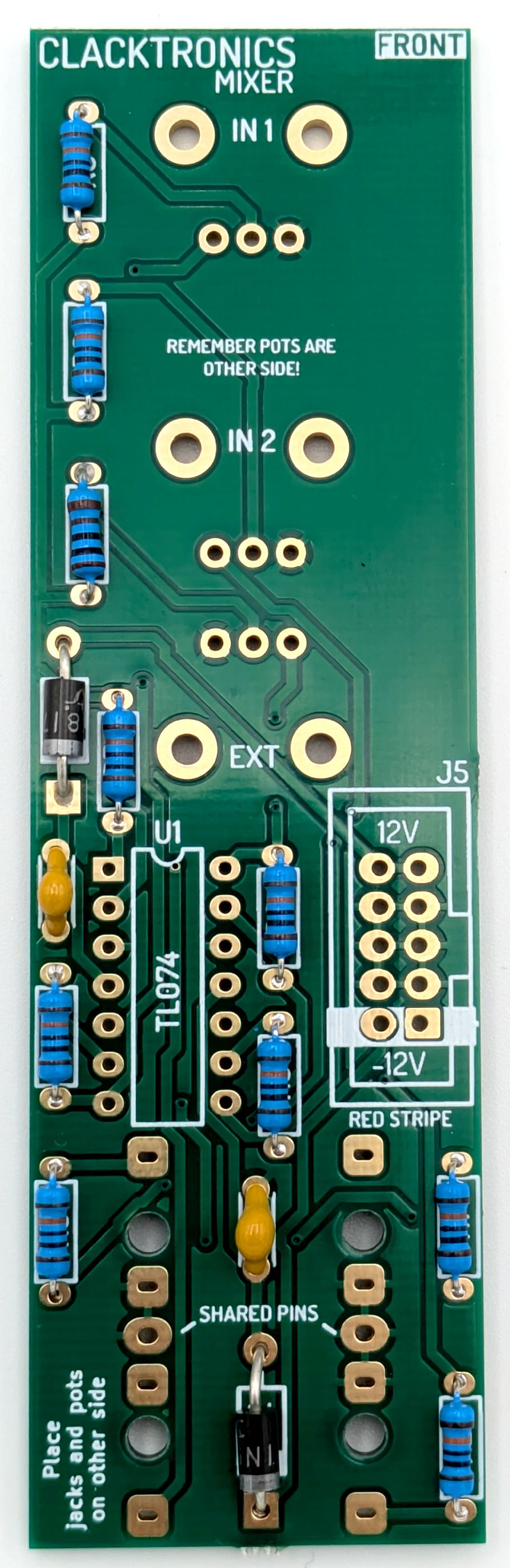
STEP 3 : DIODES
It is essential to watch orientation on these parts. Turn to the component orentation part of the ring binder for a visual representation of how the diode fits the footprint. Bend the leads down slightly wider than we are doing the resistors, these footprints are bigger because the leads on the component are quite chunky.
STEP 4 : IC SOCKET AND IDC SOCKET
Both of these parts are important to get the right way around. Look at the board to see how they are orientated, again this needs to be on the "FRONT". To solder the IC socket (U1), bend the pins out a little so it grips so you don't have to hold it in when soldering.
For The IDC socket you can't bend the pins because they are short and thick, instead hold in in the PCB and tack a pin at each end, then inspect to see if it is in properly, then solder all the pins. IDC sockets are also orientated only one way around, refer to the orientation section of the book.
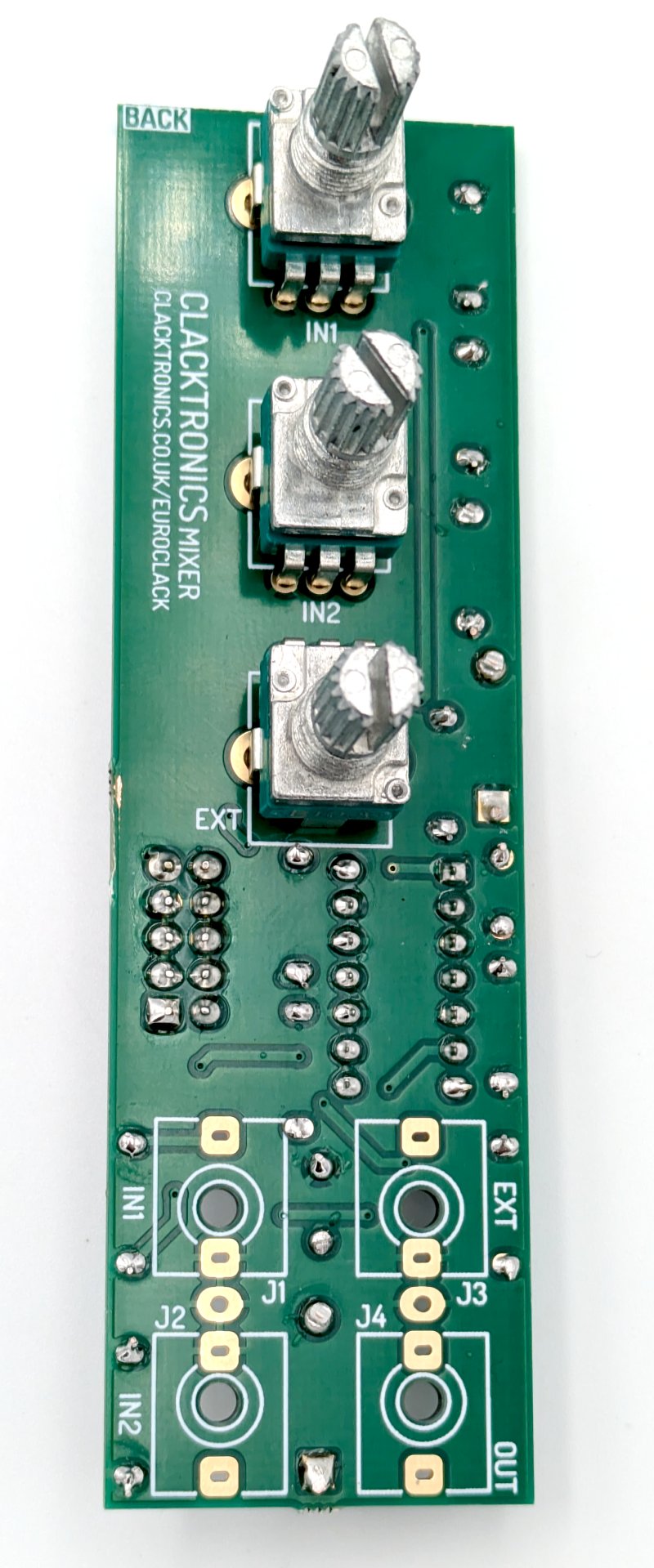
STEP 5 : FLIP OVER AND FIT THE POTS
Everything so far has been on the "FRONT", now we have to flip it over and fit the potentiometers. They should fit into their sockets snugly and hold themselves, so you do not need to hold them down to solder. Feed plenty of solder onto the large mounting pads and really heat it up, that will ensure they are soldered with a strong bond to the board, as this is how the PCB holds onto the panel.

STEP 6 : JACKS
Now fit the jack connectors on the "BACK" of the PCB. Note that the jacks share a pin with each other, you must put both jacks in when soldering them, see picture how the pins share a pad. These parts do not hold into their footprints on the PCB very tightly, I recommend soldering one pin then making sure the other is held in when soldering the other pad. Then going back and re-melting the first pad and push the jack in so it is tight against the board.

STEP 7 : PUT IN IC
Watch the orientation of the IC, it should be facing upwards if looking at the FRONT of the PCB in the socket. You will need to bend the pins straight, using a special tool or by bending them on a desk surface.
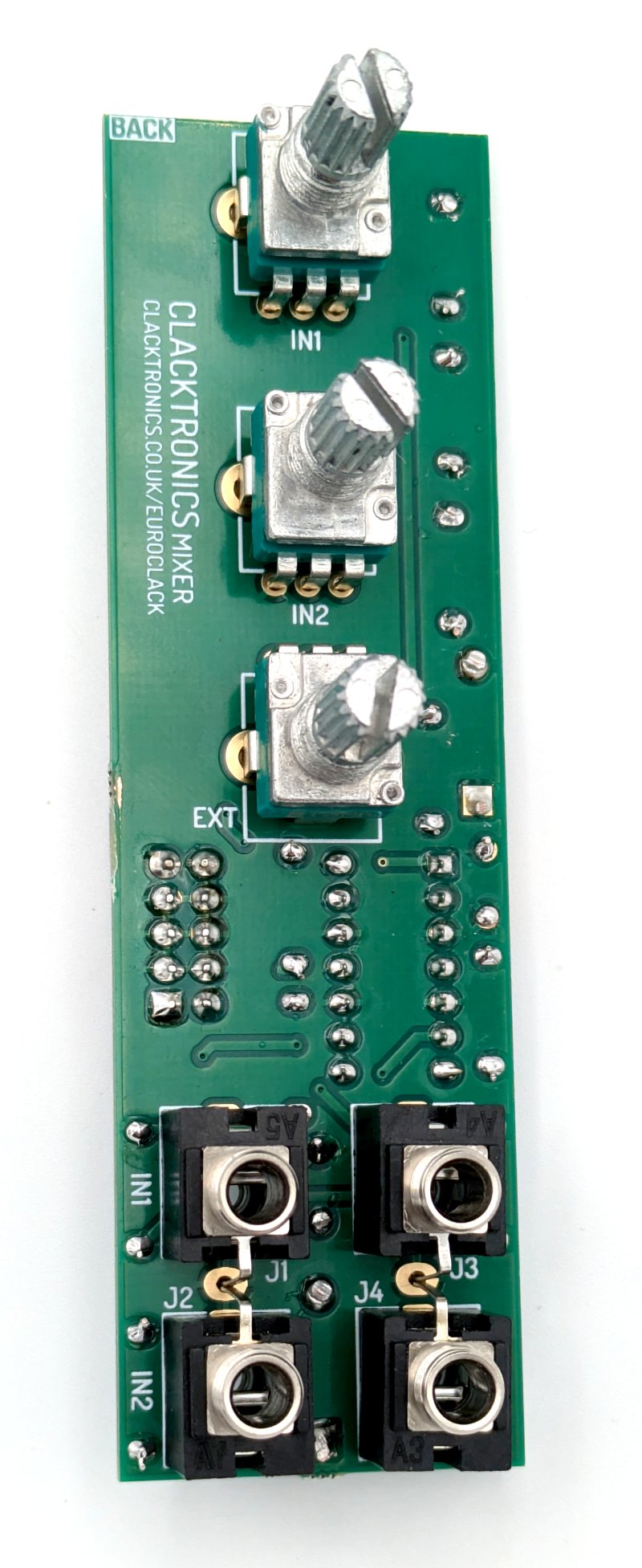
STEP 8 : PANEL ON
The panel should fit over the pots and jack on the "BACK" of the PCB. Use the provided nuts that come with these parts to fit them onto the panel. Finally place the knobs onto the potentiometers, the pointer should point bottom left when fully counter-clockwise and be bottom right when fully clockwise.
STEP 9 : PREFLIGHT
Follow the follwing checks to make sure that no damage could be made to the board.
- Before plugging in, put a multimeter in ohmic or "beep" mode, and test across the +12V, -12V and GND inputs, this should tell you if there are shorts.
- Really inspect the board closely and use your iron to melt any pads that look a bit odd or poorly covered, you should see no gold showing through on the pad.
TROUBLESHOOTING
I highly reccomend you join the Discord server as there is plenty of help there, with forums set up per-module so you can see what other people have been struggling with.
- Look at all the solder joints. Do they look fine to you? Make sure there is no bridging between pads and there are no dry joints. When starting out this is the most common point of failure. This check can also save a component that could be damaged by a short. The pad should be fully filled with solder showing no gold.
- Check and check again that you got everything in the right orientation and the right value, especially if the diodes are reversed, nothing will power then!